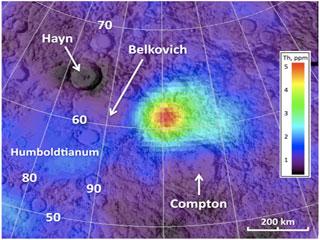
This image from NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter shows a region on the far side of the moon between the Compton and Belkovich craters. Photo: NASA.
WASHINGTON (BNS): Researchers have found a new image on the far side of the Moon, which resembles a set of dormant volcanoes on the surface of the lunar body, according to a report.
Data and photos from NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) reveal the presence of now-dead silicate volcanoes, not the more common basaltic volcanoes that litter the moon's surface, researchers said.
As the moon's rotation has been affected by tidal forces between the Earth and the moon, only one side of the moon is visible from the Earth.
NASA's Lunar Prospector probe circled the moon in 1998, it revealed a highly reflective plain lying between two ancient impact craters known as the Compton-Belkovich region, this part of the moon contains thorium and other silicate rocks.
Scientists have known for years that volcanoes on the moon filled in craters to form the dark maria visible from Earth's surface. However, those lava flows are basaltic in nature.
"This small volcanic complex occurs far away from the part of the moon where most of the volcanic activity was concentrated, and where other silicic volcanism occurred," Space.com quoted primary author Brad Jolliff of Washington University as saying.
Jolliff and his team estimated the age of the moon's rare far side silicate volcanoes to be about 800 million years old. Such an age would extend the volcanic activity of the moon by 200 million years, they said.
 Previous Article
Previous Article Next Article
Next Article












The Indian Air Force, in its flight trials evaluation report submitted before the Defence Ministry l..
view articleAn insight into the Medium Multi-Role Combat Aircraft competition...
view articleSky enthusiasts can now spot the International Space Station (ISS) commanded by Indian-American astr..
view article