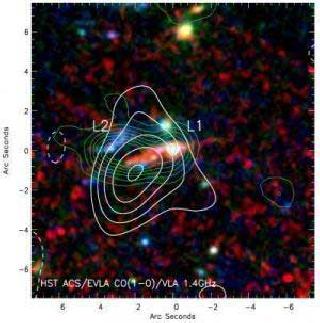
The white contours show the new measurements of carbon emissions, which have led to a drastic reassessment of the gas mass of these young galaxies. Photo: Ivison et al. 2010)
COPENHAGEN, DENMARK (BNS): Scientists from Niels Bohr Institute have studied the distant galaxies, which form around 1,000 new stars a year -- a 1,000 times more than our own galaxy, the Milky Way, according to a report.
These galaxies are the most active star-forming galaxies in the Universe.
Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society has published the findings in their research journals.
"The galaxies are located in the far distant Universe -- when the universe was 3 billion years old (equivalent to only 20 percent of its current age). It is a period of the Universe when the galaxies were very active, almost teenager-like and out of control," Science Daily quoted Thomas R. Greve, Associate professor in astrophysics at Dark Cosmology Centre, Niels Bohr Institute at the University of Copenhagen as saying.
According to the website, Thomas R. Greve has studied distant galaxies with the support of researchers from Expanded Very Large Array (an astronomical observatory in New Mexico) and Royal Observatory, Edinburgh and Durham University in England.
The astronomical observatory consists of 27 parabolic antennas, each of which have a diameter of 25 meters and can measure radio waves from distant objects.
Data from each antenna is combined electronically so that the final measurements have an angular resolution equivalent to a single antenna with a diameter of 36 km and sensitivity equal to that of a single antenna with a diameter of 130 meters.
"We have measured the CO levels, that is to say carbon monoxide, which is one of the most common molecules in the universe, after the hydrogen molecule, H2. Using the measurements we have calculated how much gas there is in the galaxy and it turns out there are extremely large amounts of gas in these galaxies," he added.
Gas is the raw material used in the Universe to form stars.
Our galaxies are almost filled with gases, these gases becomes so dense that they collapses into a ball of glowing gas, which forms a new star -- the cloud almost 'explodes' in a cosmic firework display of new stars.
The measurements of the morphology of the gas also suggest that these galaxies are usually bigger in size and irregular in shape.
After developing for several hundred of billion years, these galaxies transform into an intense star and become mature, regular, elliptical shaped galaxies like Milky Way.
 Previous Article
Previous Article Next Article
Next Article












The Indian Air Force, in its flight trials evaluation report submitted before the Defence Ministry l..
view articleAn insight into the Medium Multi-Role Combat Aircraft competition...
view articleSky enthusiasts can now spot the International Space Station (ISS) commanded by Indian-American astr..
view article