A composite image detailing the pre-life story of a star like the Sun, spanning about 10 million years from conception to birth. Photo: University of British Columbia.
TORONTO (PTI): Using satellite data that works like an ultrasound, scientists have come up with a way to determine the internal structure, age and different life stages of a star.
An international team of researchers has been monitoring the "heartbeats" of baby stars to test theories of how the Sun was born 4.5 billion years ago.
The team of 20 scientists describes how data from two space telescopes - the Canadian Space Agency's MOST satellite and the French CoRoT mission - has unveiled the internal structures and ages of young stars before they've even emerged as full-fledged stars.
"Think of it as ultrasound of stellar embryos," said University of British Columbia Professor Jaymie Matthews, MOST Mission Scientist and a co-author of the study.
"Stars can vibrate due to sound waves bouncing inside. We detect the sound vibrations across the vacuum of space by the subtle changes in stellar brightness. Then we translate the frequencies of those vibrations into models of the structures of those stars' hidden interiors," Matthews said.
Dr Konstanze Zwintz, from the KU Leuven Institute of Astronomy in Belgium and lead author of the study, calls this technique of probing protostars with sound waves "echography."
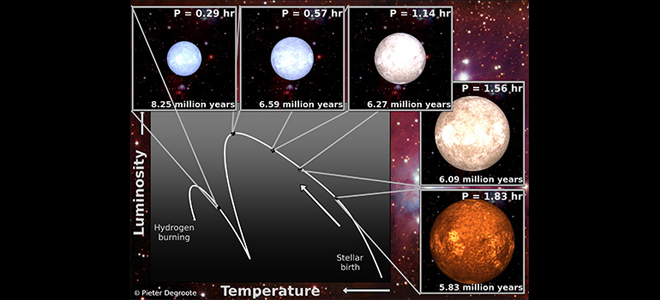
Astronomers are using measurements of this 'heartbeat' as a virtual time machine to explore the life stages of a star.
The study found that when an emerging star is closer to the initial stage of its formation (as in the first trimester of a human pregnancy), it pulsates slowly.
When it gets closer to igniting thermonuclear fusion in its core to become a true star (like the moment of human birth), it pulsates ever faster.
And when the hydrogen fuel at the core of a star is exhausted, it enters the last stages of its life.
Watching soon-to-be-stars in young clusters like NGC 2264, the focus of the study, is like watching our Sun during its birth, said Matthews.
The study was published in Science magazine.
 Previous Article
Previous Article Next Article
Next Article













The Indian Air Force, in its flight trials evaluation report submitted before the Defence Ministry l..
view articleAn insight into the Medium Multi-Role Combat Aircraft competition...
view articleSky enthusiasts can now spot the International Space Station (ISS) commanded by Indian-American astr..
view article