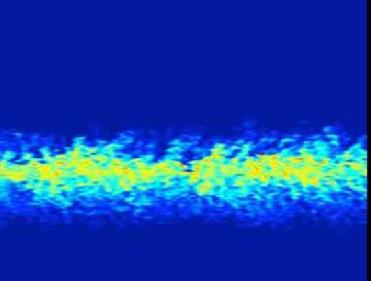
An image showing how turbulent forces mix up the layers of dust and gas orbiting young stars. San Francisco State University photo
NEW YORK (BNS): New study conducted by San Francisco State University assistant professor Joseph Barranco suggests that turbulence plays a critical role in creating ripe conditions for the birth of planets. The study, �Three-Dimensional Simulations of Kelvin-Helmholtz Instability in Settled Dust Layers in Protoplanetary Disks�, to be published in the January 20 issue of The Astrophysical Journal, challenges the prevailing theory of planet formation.
�Using three-dimensional simulations of the dust and gas that orbits young stars, the study demonstrates that turbulence is a significant obstacle to gravitational instability, the process that scientists have used since the 1970s to explain the early stage of planet formation,� The San Francisco University said.
The University said that gravitational instability proposes that dust will settle into the middle of the proto-planetary disk around a newly-formed star. It is thought that the dust will gradually become denser and thinner until it reaches a critical point and collapses into kilometer-size clumps, which later collide to form planets. But new research by Barranco shows that turbulent forces keep the dust and gas swirling and prevent it from forming a dense and thin enough layer for gravitational instability to occur.
�These results defy the proposed solution of how planets are formed. Scientists have long been using gravitational instability theory to explain how millimeter-size particles grow to kilometer-size, but these new simulations open new avenues of investigation. Perhaps massive storms, similar to hurricanes found on the Earth or Jupiter, provide clues about how tiny dust grains clump together to become kilometer-size boulders,� Barranco said.
According to the University, previous studies had used two-dimensional models to simulate the orbiting dust and gas around young stars, which failed to take account of a crucial force that causes turbulence: the Coriolis Effect. The first to use three-dimensional models, Barranco investigated the Coriolis Effect, the same mechanism that produces cyclones and tornadoes on Earth, and vertical shear. Vertical shear occurs because the faster-moving dust settles into the middle of the orbiting plane with the slower-moving gas above and below it. The velocity difference between the dust and gas causes waves to form, similar to when wind blows over the surface of water, the University said.
�What happens to the dust and gas after a period of turbulence is still an open question. But it could be that in the quiet center of a hurricane-like storm, dust can collect and get trapped, seeding the beginnings of planet formation,� Barranco said.
 Previous Article
Previous Article Next Article
Next Article













The Indian Air Force, in its flight trials evaluation report submitted before the Defence Ministry l..
view articleAn insight into the Medium Multi-Role Combat Aircraft competition...
view articleSky enthusiasts can now spot the International Space Station (ISS) commanded by Indian-American astr..
view article