
Composite image of JKCS041, the most distant galaxy cluster ever detected. Image credit:NASA
WASHINGTON (BNS): Date obtained from NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory and optical and infrared telescopes have enabled astronomers to spot the most distant galaxy cluster located about 10.2 billion light years away.
The galaxy cluster, known as JKCS041, beats the previous record holder – XMMXCS J2215.9 –by about a billion light years. It is observed as it was when the Universe was only about a quarter of its present age, NASA said.
XMMXCS J2215.9, discovered by ESA's XMM-Newton in 2006, is located 9.2 billion light years away.
“This discovery is exciting because it is like finding a Tyrannosaurus Rex fossil that is much older than any other known. One fossil might just fit in with our understanding of dinosaurs, but if you found many more, you would have to start rethinking how dinosaurs evolved. The same is true for galaxy clusters and our understanding of cosmology,” said co-author Ben Maughan, from the University of Bristol in the UK.
Studying the cosmic body’s various aspects such as its composition, mass and temperature will help scientists understand more about how the Universe evolved.
“This object is close to the distance limit expected for a galaxy cluster. We don't think gravity can work fast enough to make galaxy clusters much earlier,” said Stefano Andreon of the National Institute for Astrophysics (INAF) in Milan, Italy.
The component galaxies of JKCS041 were first detected in 2006 by the United Kingdom Infrared Telescope (UKIRT). Its distance was then determined from optical and infrared observations from UKIRT, the Canada-France-Hawaii telescope in Hawaii and NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope.
Data obtained from the Chandra X-ray provide crucial evidence that JKCS041 is indeed a “genuine galaxy cluster”, the US space agency said. The extended X-ray emission seen by Chandra shows that hot gas has been detected between the galaxies, as expected for a true galaxy cluster rather than one that has been caught in the act of forming.
Also, without the X-ray observations, the possibility remained that this object could have been a blend of different groups of galaxies along the line of sight, or a filament, a long stream of galaxies and gas, viewed front on. The mass and temperature of hot gas detected rule out both of the alternatives.
 Previous Article
Previous Article Next Article
Next Article
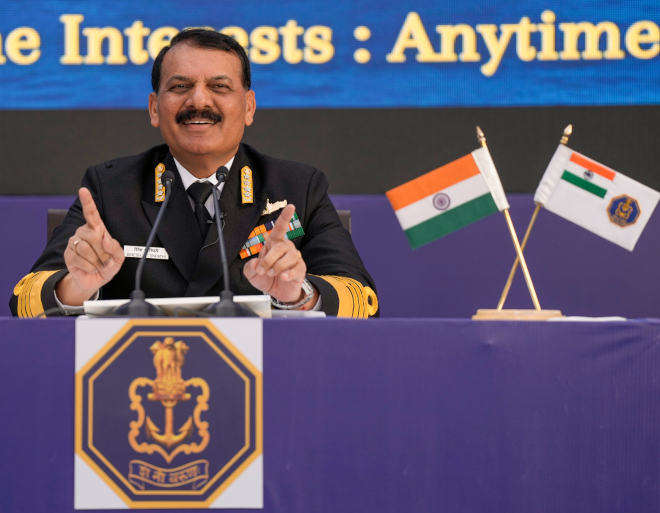
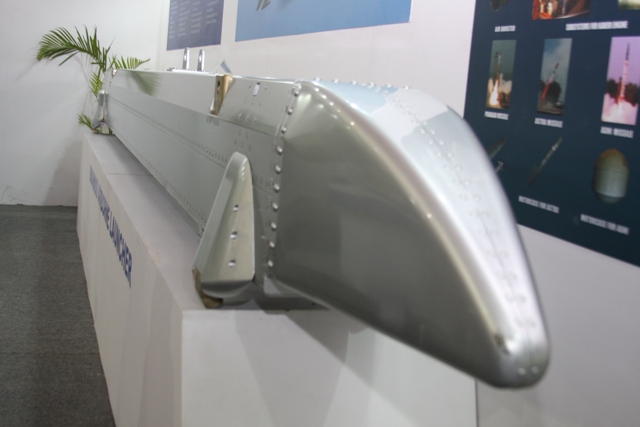











The Indian Air Force, in its flight trials evaluation report submitted before the Defence Ministry l..
view articleAn insight into the Medium Multi-Role Combat Aircraft competition...
view articleSky enthusiasts can now spot the International Space Station (ISS) commanded by Indian-American astr..
view article