
The galaxy 'UDFy-38135539' which was first spotted by Hubble telescope in 2009. An ESO photo
PARIS (BNS): Astronomers using ESO’s Very Large Telescope have measured the distance of a galaxy, which according to them, is the most remote object identified in the Universe so far.
The faint glow coming from the galaxy ‘UDFy-38135539’ which lies in the Ultra Deep Field search area in the constellation Fornax, indicates that it is seen just 600 million years after Big Bang.
“Using the ESO Very Large Telescope we have confirmed that a galaxy spotted earlier using Hubble is the most remote object identified so far in the Universe,” Matt Lehnert, lead author of the paper reporting the results, said.
These are the first confirmed observations of a galaxy whose light is clearing the opaque hydrogen fog that filled the early Universe – a period called the “era of reionisation.” During this phase, the Universe was not fully transparent as much of it was filled with the hydrogen fog that absorbed the fierce ultraviolet light from young galaxies.
While analysing the results, the researchers also found that the glow from UDFy-38135539 was not strong enough to entirely clear the hydrogen fog.
“There must be other galaxies, probably fainter and less massive nearby companions of UDFy-38135539, which also helped make the space around the galaxy transparent. Without this additional help the light from the galaxy, no matter how brilliant, would have been trapped in the surrounding hydrogen fog and we would not have been able to detect it,” co-author Mark Swinbank said.
The new findings appear in the latest issue of the journal Nature.
 Previous Article
Previous Article Next Article
Next Article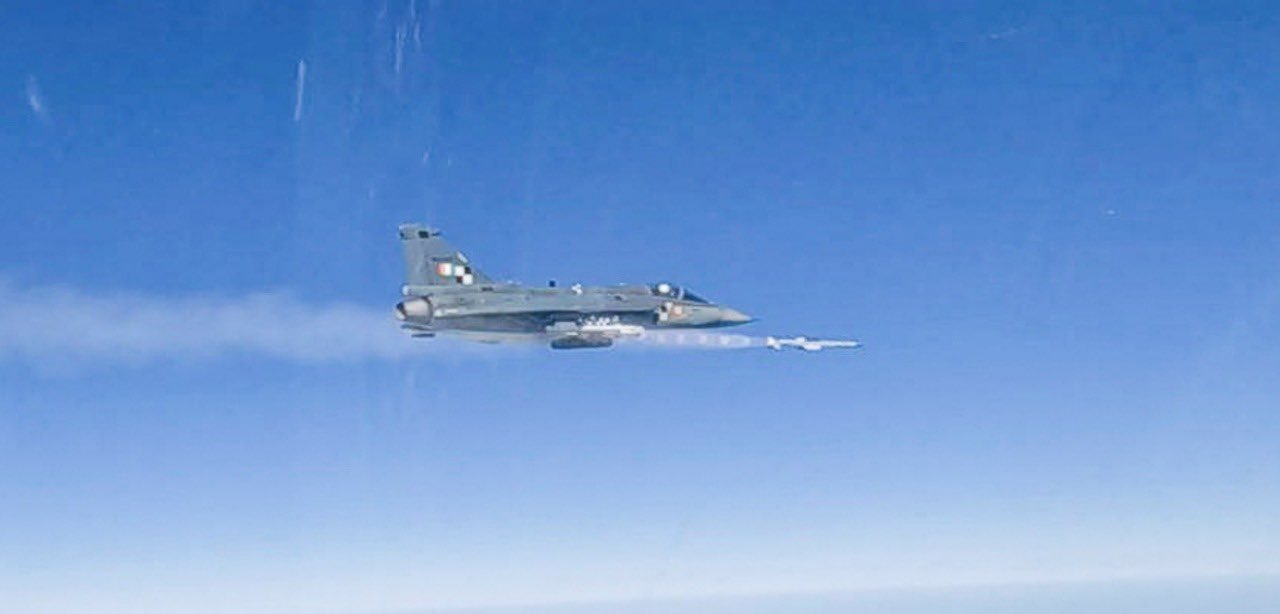












The Indian Air Force, in its flight trials evaluation report submitted before the Defence Ministry l..
view articleAn insight into the Medium Multi-Role Combat Aircraft competition...
view articleSky enthusiasts can now spot the International Space Station (ISS) commanded by Indian-American astr..
view article