Astronomers have obtained exceptional 3D views of distant galaxies, seen when the Universe was half its current age. ESO image
PARIS (BNS): For the first time, astronomers with the help of NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope’s acute eye have captured the 3D views of distant galaxies, seen when the Universe was half its current age. Researchers feel that with the capacity of ESO’s Very Large Telescope they will be able to probe the motions of gas in tiny objects and also solve the puzzle of how galaxies were formed in the remote past at a time when the Sun and the Earth did not exist.
François Hammer, who led the team of researchers, said that the unique combination of Hubble and VLT allows modeling of distant galaxies almost as nicely as the close ones.
“In effect, FLAMES/GIRAFFE now allows us to measure the velocity of the gas at various locations in these objects. This means that we can see how the gas is moving, which provides us with a three-dimensional view of galaxies halfway across the Universe,” François Hammer said.
The European Space Agency said that the team had undertaken the major task of reconstituting the history of about 100 remote galaxies that had been observed with both Hubble and GIRAFFE on the VLT. The first results have provided useful insights for three galaxies, the agency said. It also noted that the same will be featured in Astronomy and Astrophysics journal soon.
Mathieu Puech, researcher reporting the study said that in one galaxy, GIRAFFE revealed a region full of ionised gas, that is, hot gas composed of atoms that have been stripped of one or several electrons. “This is normally due to the presence of very hot, young stars. However, even after staring at the region for more than 11 days, Hubble did not detect any stars! Clearly this unusual galaxy has some hidden secrets,” Puech said.
The researcher says that comparisons with computer simulations suggest that the explanation lies in the collision of two very gas-rich spiral galaxies. The heat produced by the collision would ionise the gas, making it too hot for stars to form, he said.
ESA said that another galaxy that the astronomers studied showed the opposite effect. There they discovered a bluish central region enshrouded in a reddish disc, almost completely hidden by dust. “The models indicate that gas and stars could be spiralling inwards rapidly. This might be the first example of a disc rebuilt after a major merger,” says Hammer
Finally, in a third galaxy, the astronomers identified a very unusual, extremely blue, elongated structure, a bar, composed of young, massive stars, rarely observed in nearby galaxies. Comparisons with computer simulations showed the astronomers that the properties of this object are well reproduced by a collision between two galaxies of unequal mass, the space agency said.
“The unique combination of Hubble and FLAMES/GIRAFFE at the VLT makes it possible to model distant galaxies in great detail, and reach a consensus on the crucial role of galaxy collisions for the formation of stars in a remote past,” Puech adds.
Meanwhile, another researcher, Sébastien Peirani says that it is because we can now see how the gas is moving that we can trace back the mass and the orbits of the ancestral galaxies relatively accurately. “Hubble and the VLT are real ‘time machines’ for probing
the Universe’s history,” Peirani said.
The space agency said that the astronomers are now extending their analysis to the whole sample of galaxies observed. “The next step will then be to compare this with closer galaxies, and so, piece together a picture of the evolution of galaxies over the past six to eight billion years, that is, over half the age of the Universe,” Hammer concluded.
 Previous Article
Previous Article
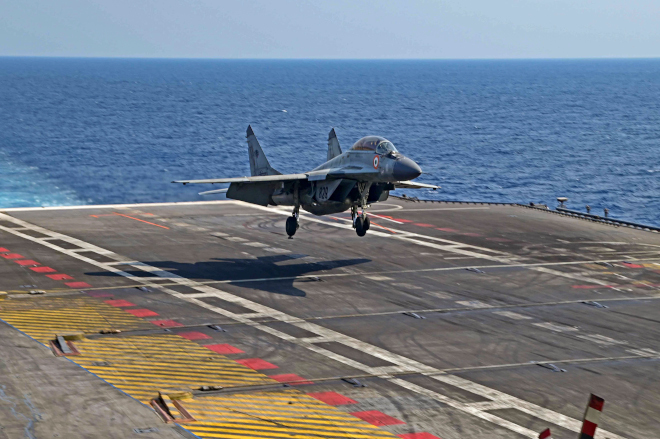
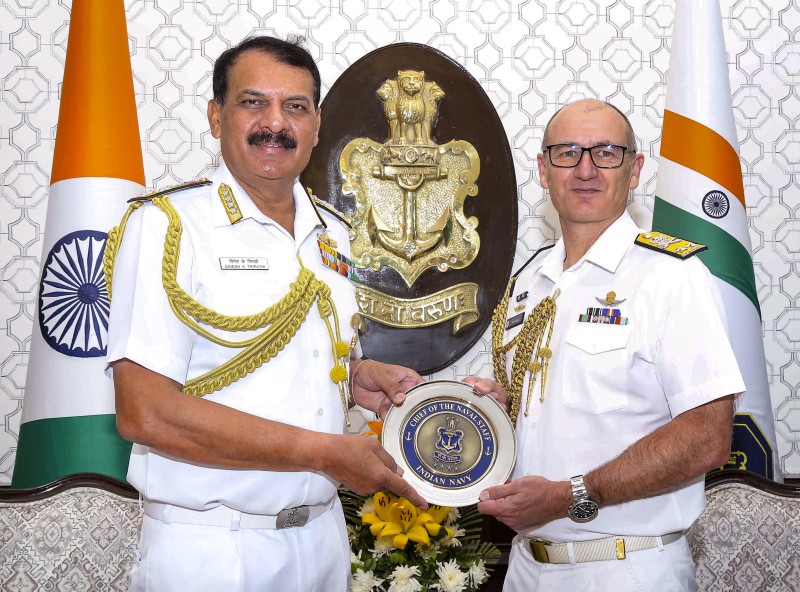












The Indian Air Force, in its flight trials evaluation report submitted before the Defence Ministry l..
view articleAn insight into the Medium Multi-Role Combat Aircraft competition...
view articleSky enthusiasts can now spot the International Space Station (ISS) commanded by Indian-American astr..
view article