
GSLV-F04 prior to launch. Image credit: ISRO
The Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV) is a communication satellite launcher operated by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). It was developed to enable India to launch its INSAT-type satellites into geostationary orbit.
Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV) Mark I & II are capable of placing INSAT–II class of satellites (2000 kg to 2,500 kg) into Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO).
The three-stage GSLV vehicle is 49 meter tall with a lift off weight of 414 tones. It has a maximum diameter of 3.4 meter at the payload fairing. First stage comprises S125 solid booster with four liquid (L40) strap-ons. Second stage (GS2) is liquid engine and the third stage (GS3) is a cryo stage. The vehicle develops a lift off thrust of 6573 kn.
The first flight of GSLV took off from Sri Harikota space centre on April 18, 2001 by launching 1540 kg GSAT-1. It was followed by four more launches – GSLV-D2 on May 8, 2003 (1825 kg), GSLV-F01 on September 20, 2004 (EDUSAT 1950 kg), GSLV-F02 on July 10, 2006 and GSLV-F04 on September 2, 2007 (INSAT-4CR 2130 kg).
GSLV-III.
The GSLV-III or Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mark III is a launch vehicle currently under development by ISRO. The latest version of the launch vehicle is being designed to make ISRO fully self-reliant in launching heavier communication satellites of INSAT-4 class, which weigh 4500 kg to 5000 kg. The vehicle envisages multi-mission launch capability for GTO, LEO, Polar and intermediate circular orbits.
The 42.2 meter tall GSLV-Mk III is being designed to be a three stage vehicle, with a lift off weight of 630 tonnes. First stage comprises two identical S200 Large Solid Booster (LSB) with 200 tonne solid propellant, that are strapped on to the second stage – the L110 re-startable liquid stage.
The third stage is the C25 LOX/LH2 cryo stage. The large payload fairing measures 5 meter in diameter and can accommodate a payload volume of 100 cu m. The development work on Mk III is progressing as per schedule for a launch in 2011.
ISRO is also planning to launch the country's communication satellite GSAT-4 with its Geo-synchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle – GSLV-D3, by December 2009.
- Courtesy:
ISRO
 Previous Article
Previous Article Next Article
Next Article
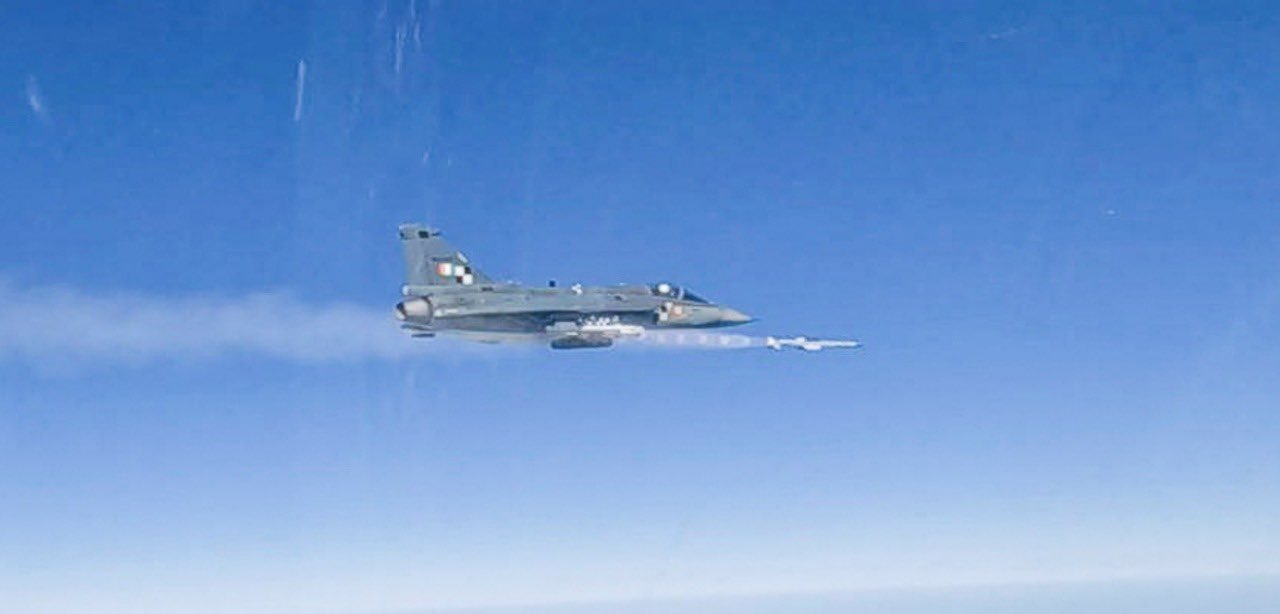










The Indian Air Force, in its flight trials evaluation report submitted before the Defence Ministry l..
view articleAn insight into the Medium Multi-Role Combat Aircraft competition...
view articleSky enthusiasts can now spot the International Space Station (ISS) commanded by Indian-American astr..
view article