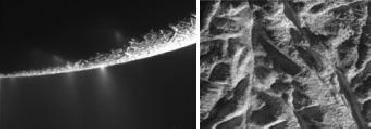
This unprocessed image captured by NASA's Cassini spacecraft shows Saturn�s moon Enceladus� south polar region where jets of water vapor and other particles spew from fissures on the surface. (Right) The ridges and fractures on the surface of the icy moon. Image credit: NASA/JPL/Space Science Institute
WASHINGTON (BNS): The intriguing �tiger stripe� region in Saturn�s moon Enceladus will now be studied in greater detail by scientists who have obtained high-resolution images of the southern part of the moon�s Saturn-facing hemisphere.
NASA�s Cassini spacecraft, in its eighth targeted flyby of Enceladus on November 21, has transmitted uncalibrated temperature data and images of the �rippling terrain� of the distant planet�s moon.
�These first raw images are spectacular, and paint an even more fascinating picture of Enceladus. The Cassini teams will be delving into the data to better understand the workings of this bizarre, active moon,� said Bob Pappalardo, Cassini project scientist at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena.
The tiger stripes are fissure in the south polar region which spew jets of water vapour and other particles hundreds of kilometers from the surface.
The spacecraft�s flyby, which brought it within about 1,600 kilometers of Enceladus�s surface, was the scientists' last peek at the tiger stripes before the south pole fades into the darkness of winter for several years, NASA said.
Cassini is now heading towards Rhea, another moon, for more imaging and mapping work.
 Previous Article
Previous Article Next Article
Next Article













The Indian Air Force, in its flight trials evaluation report submitted before the Defence Ministry l..
view articleAn insight into the Medium Multi-Role Combat Aircraft competition...
view articleSky enthusiasts can now spot the International Space Station (ISS) commanded by Indian-American astr..
view article