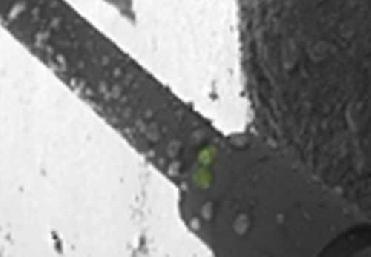
Droplets on a leg of the Mars Phoenix lander are seen to darken and coalesce. Nilton Renno, a professor in the Department of Atmospheric, Oceanic and Space Sciences says this is evidence that they are made of liquid water. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/University of Arizona/Max Planck Institute
WASHINGTON (BNS): A team of scientists led by a University of Michigan professor Nilton Renno has found salty, liquid water on a leg of the Mars Phoenix Lander. This is the first time liquid water has been detected and photographed outside the Earth. With this, scientists presume that water could be present at other locations on the planet too.
Nilton Renno, a professor in the U-M Department of Atmospheric, Oceanic and Space Sciences and a co-investigator on the Phoenix mission, said that a large number of independent physical and thermo-dynamical evidence shows that saline water may actually be common on Mars.
“Liquid water is an essential ingredient for life. This discovery has important implications to many areas of planetary exploration, including the habitability of Mars,” Renno said.
Renno will present these findings at the Lunar and Planetary Science Conference in Houston on Monday. Renno said that earlier, scientists thought that water existed on Mars only as ice or water vapour because of the planet's low temperature and atmospheric pressure. They thought that ice in the Red Planet’s current climate could sublimate, or vapourise, but they didn’t think it could melt, he said.
The professor said that this analysis shows how that assumption may be incorrect.
“Temperature fluctuation in the arctic region of Mars where Phoenix landed and salts in the soil could create pockets of water too salty to freeze in the climate of the landing site,” Renno said.
The scientist said that the photos of one of the lander's legs show droplets that grew during the polar summer. Based on the temperature of the leg and the presence of large amounts of ‘perchlorate’ salts detected in the soil, the droplets were most likely salty liquid water and mud that splashed on the spacecraft when it touched down, the scientists said. The lander was guided down by rockets whose exhaust melted the top layer of ice below a thin sheet of soil, they added.
Some of the mud droplets that splashed on the lander's leg appear to have grown by absorbing water from the atmosphere, Renno says, adding that images suggest that some of the droplets darkened, then moved and merged -- physical evidence that they were liquid.
According to NASA, the wet chemistry lab on Phoenix found evidence of perchlorate salts, which likely include magnesium and calcium perchlorate hydrates. These compounds have freezing temperatures of about -90 and -105 Fahrenheit respectively.
The temperature at the landing site ranged from approximately -5 to -140 Fahrenheit, with a median temperature around -75 Fahrenheit. Temperatures at the landing site were mostly warmer than this during the first months of the mission, NASA said.
Scientists state that thermodynamic calculations offer additional evidence that salty liquid water can exist where Phoenix landed and elsewhere on Mars. The calculations also predict a droplet growth rate that is consistent with what was observed. And they show that it is impossible for ice to sublimate from the cold ground just under the strut of the lander's leg and be deposited on a warmer strut, a hypothesis that has been suggested by scientists. Certain bacteria on Earth can exist in extremely salty and cold conditions, they said.
“This discovery is the result of the talent and dedication of the entire Phoenix team and NASA, whose strategy for Mars exploration and the Phoenix mission is follow the water,” Renno said.
 Previous Article
Previous Article Next Article
Next Article
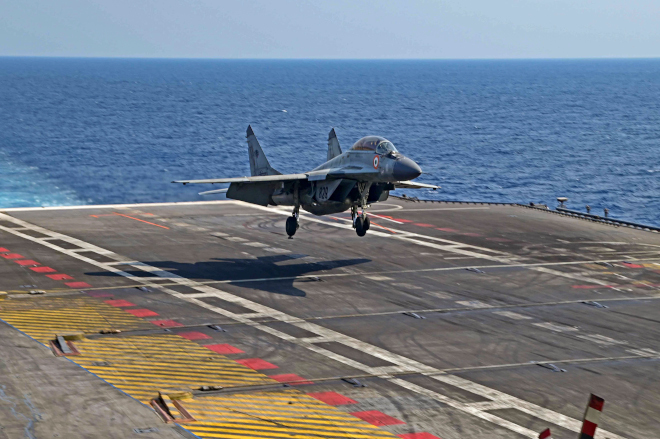
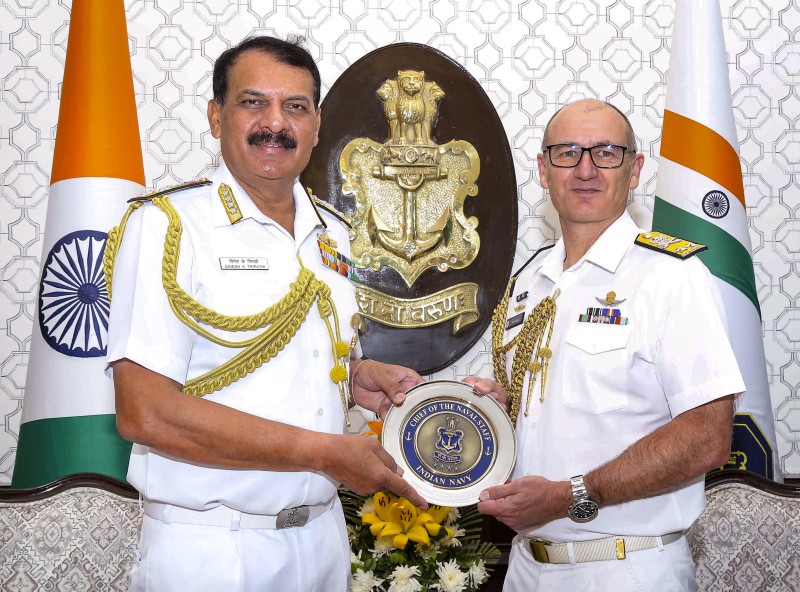













The Indian Air Force, in its flight trials evaluation report submitted before the Defence Ministry l..
view articleAn insight into the Medium Multi-Role Combat Aircraft competition...
view articleSky enthusiasts can now spot the International Space Station (ISS) commanded by Indian-American astr..
view article